Introduction
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic dream—it is reshaping the very core of how we live and work. At the center of this transformation lies a powerful innovation: the AI Agent. These digital entities are not just tools; they are autonomous decision-makers, capable of learning, adapting, and executing tasks with minimal human input.
In this article, we explore what an AI Agent truly is, how it functions, and why it’s becoming a cornerstone of the future workplace. From automating simple tasks to driving high-level strategic processes, AI Agents are becoming indispensable in nearly every industry. Whether you are a tech enthusiast, a business owner, or someone curious about how the digital world is evolving, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know.
Chapter 1: What is an AI Agent?
Understanding the Concept
An AI Agent is a type of software entity that acts on behalf of a user or a system to achieve specific goals. Unlike regular software programs that follow strict rules, an AI Agent can analyze its environment, make decisions, and take actions independently.
At its core, an AI Agent has four essential elements:
- Perception – It gathers information from the environment.
- Decision-making – It interprets the data and makes logical decisions.
- Action – It performs tasks to achieve a goal.
- Learning – It improves over time by learning from previous actions and feedback.
How AI Agents Are Different
Traditional automation tools follow pre-defined scripts. If conditions change, they fail. AI Agents, on the other hand, use intelligence to adapt and continue functioning. They don’t just “do”—they “understand” and “react.” That’s the difference between a basic chatbot and a smart virtual assistant that can schedule meetings, summarize documents, or even manage workflows.
Chapter 2: The Core Capabilities of AI Agents
1. Autonomy
AI Agents operate without needing constant human oversight. They can initiate tasks, make decisions, and adjust their actions based on outcomes. This autonomy makes them suitable for real-time, dynamic environments.
2. Reasoning and Planning
They can plan multiple steps ahead. For example, an AI Agent in project management might analyze team performance, prioritize tasks, and allocate resources—all while adapting to changes.
3. Tool Integration
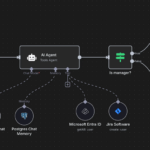
Modern AI Agents are not standalone—they integrate with APIs, databases, CRMs, and even IoT devices. This lets them retrieve data, update records, or communicate with other systems seamlessly.
4. Memory and Context Awareness
Unlike older bots, AI Agents can retain memory across sessions. This means they can understand ongoing tasks, refer back to past conversations, and improve their responses over time.
Chapter 3: Real-World Applications of AI Agents
1. Customer Support
AI Agents are widely used in customer service. They can handle common queries, route tickets, escalate complex issues, and even detect customer emotions. This improves response times and customer satisfaction.
2. Sales and Marketing
AI Agents analyze customer data, run A/B tests, create personalized campaigns, and follow up with leads. They help marketers deliver the right message at the right time, boosting conversions and ROI.
3. Healthcare
In hospitals and clinics, AI Agents assist in patient triage, appointment scheduling, medication reminders, and even preliminary diagnosis. Their ability to manage large volumes of data ensures timely and accurate healthcare delivery.
4. HR and Recruitment
From resume screening to onboarding new employees, AI Agents streamline HR tasks. They can match candidates with job roles, conduct initial assessments, and manage employee records.
5. Finance and Banking
AI Agents monitor transactions, detect fraud, offer investment advice, and handle routine banking queries. Their 24/7 availability ensures uninterrupted financial services.
Chapter 4: Benefits of AI Agents in the Workplace
1. Increased Efficiency
By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, AI Agents free up human employees to focus on strategic, creative, and decision-making roles. This leads to faster turnaround times and greater productivity.
2. Cost Reduction
Businesses can significantly reduce operational costs by deploying AI Agents. They minimize human errors, eliminate redundancy, and handle large volumes of work without demanding additional resources.
3. Enhanced Accuracy
AI Agents, powered by machine learning, make fewer mistakes than humans in tasks involving data processing, calculations, and pattern recognition. This is particularly crucial in industries like finance and healthcare.
4. 24/7 Availability
Unlike humans, AI Agents do not need breaks, sleep, or vacations. They work around the clock, ensuring continuous support and operations—especially useful in global businesses.
5. Data-Driven Insights
AI Agents analyze large sets of data in real-time. They identify trends, detect anomalies, and generate actionable insights that help businesses make informed decisions faster.
Chapter 5: How AI Agents Are Changing the Future of Work
1. Redefining Job Roles
As AI Agents take over routine and manual tasks, job roles are evolving. Employees now spend more time on creative thinking, innovation, and problem-solving. The workplace becomes less about labor and more about leadership.
2. Enabling Remote and Hybrid Work
AI Agents facilitate remote collaboration by managing schedules, tracking productivity, and automating communication. This supports the modern hybrid workforce and maintains team cohesion across time zones.
3. Supporting Decision-Making
From CEOs to team leads, professionals rely on AI Agents for data analysis and strategic planning. These agents offer simulations, forecasts, and models that improve decision-making accuracy.
4. Accelerating Innovation
With routine tasks automated, companies can invest more time and resources into innovation. AI Agents help in rapid prototyping, testing new ideas, and launching products faster than ever before.
5. Bridging Skill Gaps
AI Agents serve as digital mentors and assistants for new employees. They provide training, answer questions, and support learning, thus reducing onboarding time and helping build skills.
Chapter 6: Challenges of AI Agent Adoption
1. Job Displacement Fears
While AI Agents create new opportunities, they also raise concerns about job loss. Roles based on repetitive work are most at risk. It’s essential to balance automation with upskilling and reassigning employees.
2. Data Privacy and Security
AI Agents operate on sensitive data. Companies must ensure strong data protection policies to prevent leaks and maintain compliance with regulations like GDPR.
3. Trust and Transparency
Users often struggle to trust AI decisions, especially when outcomes are unclear. Organizations need to build transparency into AI Agents by explaining how they make decisions and offering oversight options.
4. Integration Complexity
Adding AI Agents to existing systems can be complex. Proper planning, testing, and customization are needed to ensure smooth integration and avoid disruptions.
5. Ethical Considerations
AI Agents must be programmed with ethical guidelines to avoid biased decisions. This includes fair treatment in recruitment, unbiased marketing, and accurate content generation.
Chapter 7: Preparing for an AI Agent–Powered Future
1. Upskilling the Workforce
Employees must be trained to work alongside AI. This includes technical skills (data analysis, AI usage) and soft skills (creativity, ethics, leadership) that AI can’t replicate.
2. Redefining Work Culture
Companies must adopt a culture that embraces change, continuous learning, and digital collaboration. Leaders play a critical role in encouraging adoption and easing transitions.
3. Establishing Governance Policies
Clear rules must define how AI Agents operate, who monitors them, and what limits they have. This protects both the business and its customers.
4. Partnering with AI Vendors
Rather than building everything in-house, businesses can collaborate with AI vendors for tools, training, and customization. This speeds up deployment and ensures better results.
5. Embracing Human-AI Collaboration
The most successful organizations won’t replace humans—they’ll combine human intelligence with AI Agents. This synergy will become the ultimate competitive advantage.
Conclusion
The AI Agent is not just another tech trend. It is a fundamental shift in how we think about work, productivity, and intelligence. By enabling machines to act, learn, and decide like humans—but faster and at scale—AI Agents are rewriting the rules of business and employment.
For businesses, this is a time of immense opportunity. For individuals, it’s a chance to upgrade their skills and work smarter. And for society, it’s a path toward a more efficient, creative, and connected future.
At SGK Tech Guide, we believe the future belongs to those who embrace change, and AI Agents are leading that change today. Stay informed, stay adaptable, and explore how you can benefit from the intelligent workforce of tomorrow.